In this article, you’ll discover the advanced technology and expertise involved in manufacturing thermal transfer ribbons. What might seem like a simple printing ribbon is actually designed with cutting-edge technology. These vital products, used for printing labels across multiple industries, undergo a detailed manufacturing process to ensure high quality, durability, and cost efficiency.
Made with wax, resin, or a blend of both, they work with specialized inks to provide exceptional print quality and long-lasting performance. Keep reading to learn how this process works and explore the key materials that give these ribbons their unique characteristics.
Understanding Thermal Transfer Ribbons: How do thermal transfer ribbons work?
Also referred to as TTR, thermal transfer ribbons are essential components in thermal transfer printing. Essentially, they consist of a plastic film coated on one side with ink and on the other with silicone. This silicone layer is key to the process, as it helps to dissipate heat during printing.
As the product moves through the printer and is heated, the ink is released and transferred onto the material, typically a label, forming the printed image. This highlights the ribbon’s critical role in ensuring high-quality prints.
Depending on the type, the coating can include wax, resin, or a combination of both. Each type provides distinct benefits, with wax offering high-quality prints for short-term use and resin delivering superior durability for long-lasting results. Thermal transfer ribbons are crucial for producing precise, readable, and durable labels across various industries.
What are the main uses of thermal transfer ribbons?
A thermal transfer ribbon is used primarily in thermal transfer printing, where it plays a crucial role in transferring ink onto materials such as labels, tags, and packaging. The ribbon is heated by the printer’s printhead, causing the ink to melt and transfer onto the surface of the material, creating a durable print. Thermal transfer ribbons are commonly used for printing barcodes, text, and graphics on labels that need to withstand harsh environments, such as exposure to heat, moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and retail for labeling products and inventory management.
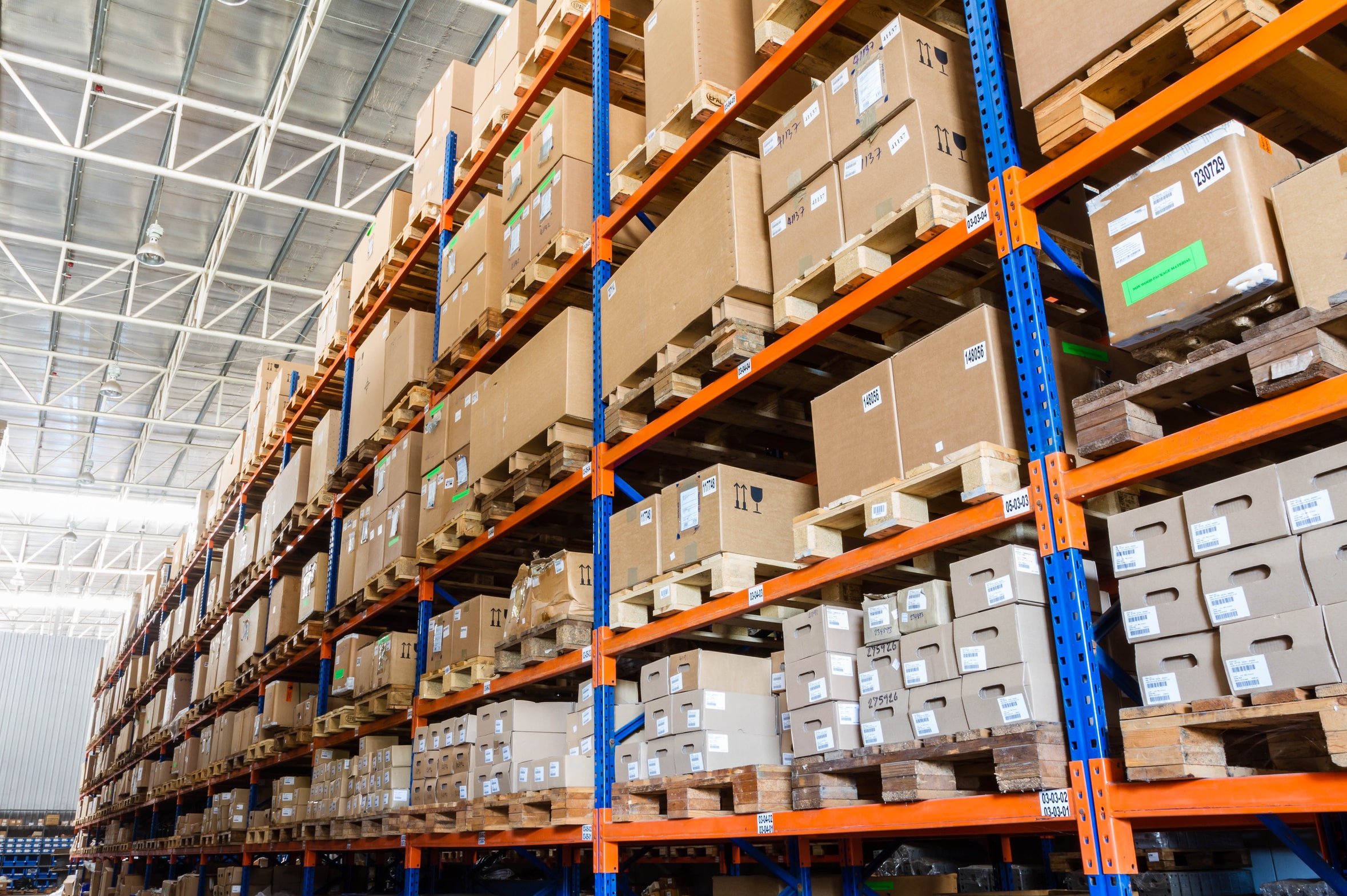
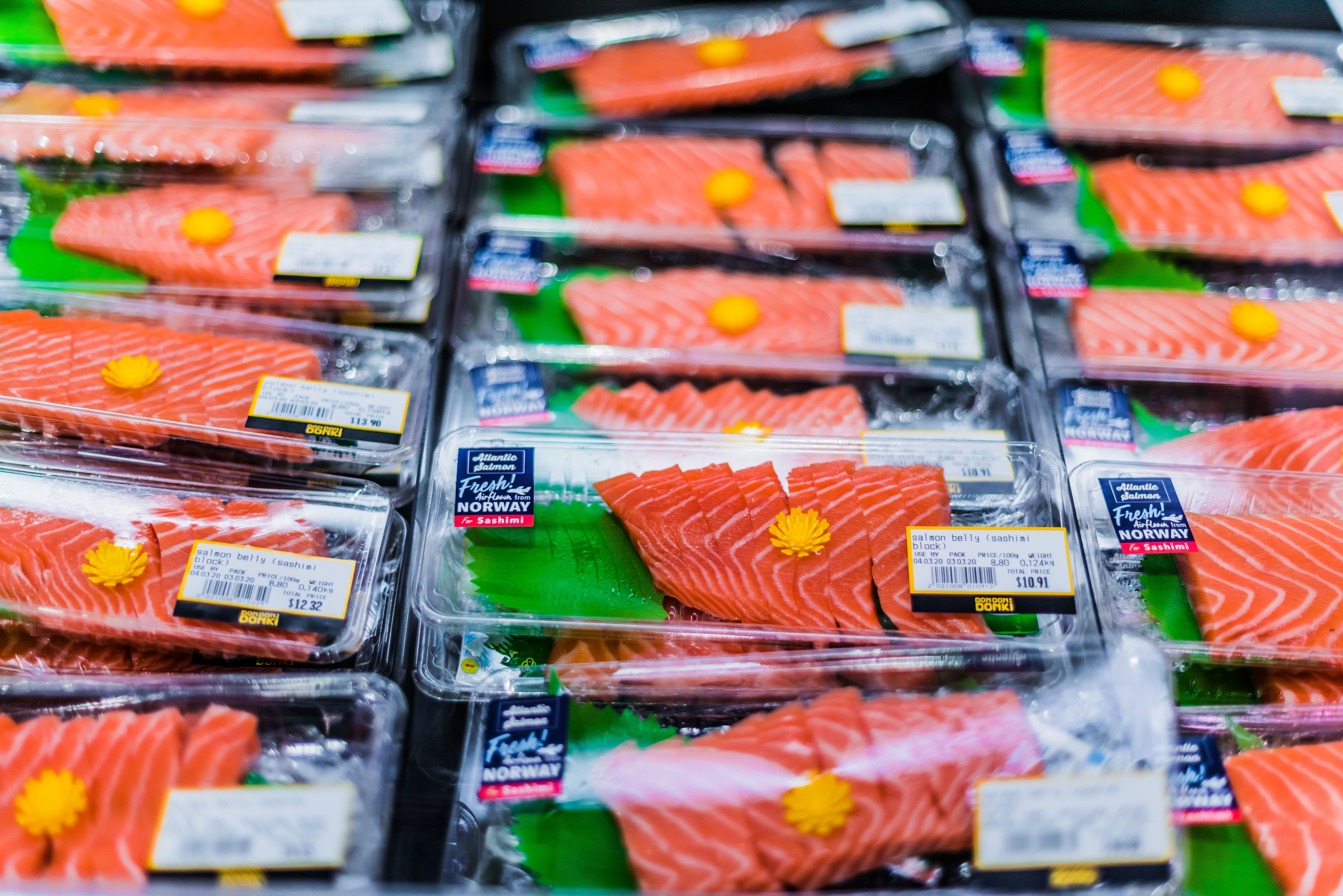
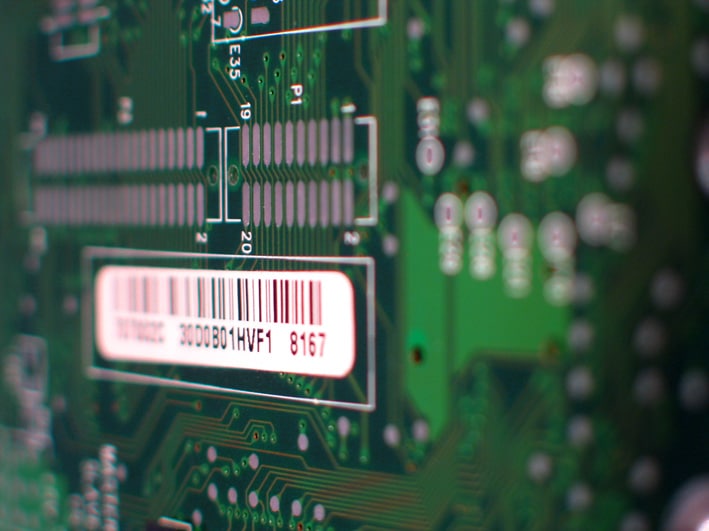



What are the differences between thermal transfer and direct thermal printing techniques?
- Thermal Transfer Printing:
In thermal transfer printing, a ribbon coated with ink is heated by the printhead. The ink is then transferred onto the material, typically a label or tag. This method produces durable prints that are resistant to fading, heat, chemicals, and abrasion, making it ideal for long-lasting labeling needs. - Direct Thermal Printing:
Direct thermal printing, on the other hand, uses heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to heat from the printhead. It does not require a ribbon. This method is faster and more cost-effective, but the prints are less durable and can fade over time, especially when exposed to heat, light, or abrasion.
What are the layers of a thermal transfer Ribbon?
This is a simplified explanation, as thermal transfer ribbons involve several other key components in their manufacturing, such as the following:
- Backcoat: A specialized technology designed to extend the life of the printhead by adding a protective silicone layer. Positioned on the back of the ribbon, it stays in contact with the printhead, protecting it from friction with the labels during the printing process.
- Release Layer: This essential layer sits between the polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and the ink. It ensures proper adhesion of the film during thermal transfer printing, enabling successful ink transfer onto the labels.
- Polyester Film (Carrier): A thin film that forms the foundation of the ribbon, providing the structure that holds the chemical layers in place. Its primary role is to maintain the integrity of the printed image during thermal transfer printing, ensuring label durability.
- Ink: The ink layer is transferred to the labels during printing. Formulated with pigment, it may contain wax, resin, or a mix of both, depending on the desired durability and print quality.
- Trailer: Located at the end of the thermal transfer ribbon, the trailer is a film that signals the printer to stop when the ribbon is nearly finished, preventing potential damage to the printer.
- Core: Made from cardboard or plastic, the core is the central shaft around which the ribbon is wound and unwound during the printing process, providing the structure necessary for smooth operation.
- Leader: A PET layer that protects the ribbon, identifies its composition, and makes it easy to load into the printer, ensuring a smooth ribbon transition during printing tasks.
What are the different types of thermal transfer ribbons?
Now that you have a clearer understanding of what thermal transfer ribbons are, it’s important to recognize that there are different types, each designed for specific uses. As these ribbons serve various applications, selecting the right model is crucial for achieving the best results. Here are the key features and uses of each type:
- Wax Ribbon: Wax ribbons are more affordable compared to other types of thermal transfer ribbons. They offer excellent performance for printing on paper materials, such as cardboard or coated paper. These ribbons are ideal for printing variable information that doesn’t need to last long, making them perfect for temporary labels or short-term applications.
- Mixed Ribbon (wax-resin ribbon): Made from a blend of wax and resin, mixed ribbons are used for products that require moderate resistance. They are perfect for applications where durability is important but won’t face the intense wear and tear found in harsher environments.
- Resin Ribbon: Resin ribbons are much more durable and expensive than wax ribbons. They are designed for labels exposed to abrasive processes, chemicals, friction, or extreme temperatures. Due to their superior durability, resin ribbons are commonly used in industries like chemicals, food, and laboratories for long-lasting labels.
- Textile Resin Ribbon: Textile resin ribbons are specifically designed to withstand domestic and industrial washing without degrading. They resist detergents and the high temperatures of dryers and irons. This makes them suitable for printing on materials used in clothing labels, ensuring high resistance in textile applications.
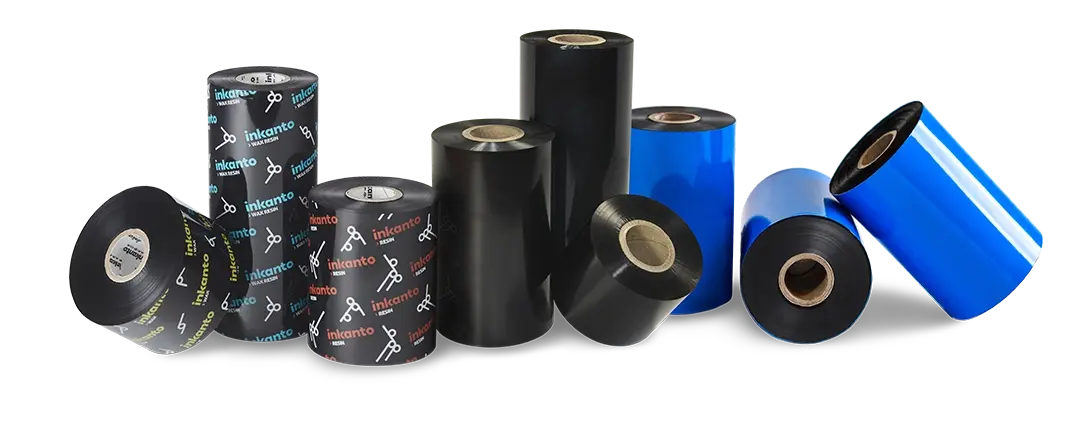

In conclusion, thermal transfer ribbons play a crucial role in producing high-quality, durable prints across a variety of industries. By understanding the different types of ribbons—wax, resin, wax-resin, and textile resin—you can choose the best option based on your specific labeling needs. Whether you require short-term labels, labels resistant to harsh environments, or those suitable for textile applications, there’s a thermal transfer ribbon designed to meet your requirements. With advancements in technology and materials, thermal transfer printing continues to provide reliable, long-lasting results for labeling, product identification, and more.
This article is brought to you by ARMOR-IIMAK a company specializing in the production of high-quality thermal transfer ribbons. With recognized expertise in the field, ARMOR-IIMAK offers a range of products tailored to various printing needs, ensuring durable and efficient solutions for multiple industries. The team at ARMOR-IIMAK is also available for any questions you may have and is ready to assist you in finding the perfect solution for your labeling needs.
